Ankylosing Spondylitis Pathogenesis
The cause of the disease is unknown. Of great importance is genetic predisposition, genetic marker which is the antigen HLA B 27, occurring in 90-95% of patients, 20-30% of their first-degree relatives and in only 7-8% in the population.
It is believed that the gene sensitivity ankylosante spondylitis is coupled with the gene HLA B 27. There are two theories of pathogenesis, explaining the important role of HLA B 27 in the development of Ankylosing Spondylitis 's disease. According to the theory of receptor antigen HLA B 27 is a receptor for the damaging etiological factor (eg, bacterial antigen, virus, artritogennogo peptide, etc.).
The resulting complex leads to production of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, which can then damage the cells or tissue area, where the molecules of the antigen in 27.
According to the theory of molecular mimicry bacterial antigen, or any other damaging agent in combination with other HLA molecule can be similar to the HLA B 27 properties and identify cytotoxic T-lymphocytes as HLA B 27 or reduce the immune response to peccant peptide (the phenomenon of immune tolerance) .
First is infiltration by lymphocytes and macrophages. And then develop active fibroplastichesky process with the formation of fibrous scar tissue, which undergoes calcification and ossification.
The main pathological manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis 's disease are inflammatory enthesiopathies (inflammation of the place of attachment to the bone tendons, ligaments, fibrous part of the intervertebral discs, capsules of the joints), inflammation of the bones forming the joint (osteitis), and synovitis.
In the subsequent develop fibrous and bony ankylosis of the joints of the axial skeleton. At least - of the peripheral joints, comes early ossification of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine.
Ankylosing Spondylitis And Mental Stress
 |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis Pathogenesis |
It is believed that the gene sensitivity ankylosante spondylitis is coupled with the gene HLA B 27. There are two theories of pathogenesis, explaining the important role of HLA B 27 in the development of Ankylosing Spondylitis 's disease. According to the theory of receptor antigen HLA B 27 is a receptor for the damaging etiological factor (eg, bacterial antigen, virus, artritogennogo peptide, etc.).
The resulting complex leads to production of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, which can then damage the cells or tissue area, where the molecules of the antigen in 27.
According to the theory of molecular mimicry bacterial antigen, or any other damaging agent in combination with other HLA molecule can be similar to the HLA B 27 properties and identify cytotoxic T-lymphocytes as HLA B 27 or reduce the immune response to peccant peptide (the phenomenon of immune tolerance) .
Ankylosing Spondylitis
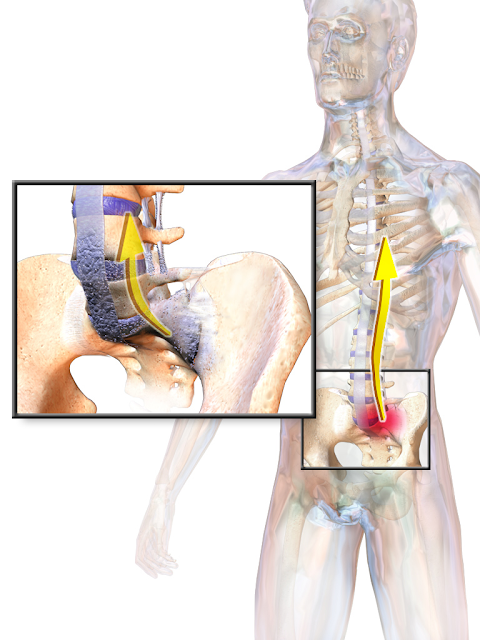
As a result, developing immunovospalitelny process. Usually it begins with the defeat of the sacroiliac joint, and then involved intervertebral, costovertebral, rarely - peripheral joints.First is infiltration by lymphocytes and macrophages. And then develop active fibroplastichesky process with the formation of fibrous scar tissue, which undergoes calcification and ossification.
The main pathological manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis 's disease are inflammatory enthesiopathies (inflammation of the place of attachment to the bone tendons, ligaments, fibrous part of the intervertebral discs, capsules of the joints), inflammation of the bones forming the joint (osteitis), and synovitis.
In the subsequent develop fibrous and bony ankylosis of the joints of the axial skeleton. At least - of the peripheral joints, comes early ossification of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine.
0 Comments